How to Approach IS-LM Curve Problems in Economics Exams
The IS-LM curve is a fundamental concept in macroeconomics that combines the equilibrium conditions of the goods market (IS curve) and the money market (LM curve). This theoretical framework is often tested in economics exams, and mastering it can significantly boost your grades. Whether you are preparing for a challenging midterm or wondering, “Can someone take my economics exam?” this comprehensive guide will help you understand how to tackle IS-LM curve problems effectively. If you need extra guidance, don’t hesitate to seek online exam help from experienced professionals.
In this blog, we will explore the theoretical aspects of the IS-LM framework and provide actionable steps to solve problems in your economics exams with ease. By the end of this detailed guide, you'll be equipped with the knowledge and confidence needed to ace IS-LM curve questions.

Understanding the IS-LM Framework
Before diving into problem-solving techniques, it is crucial to understand the theoretical foundation of the IS-LM model. Let’s break down the two core components of this framework.
What is the IS Curve?
The IS curve represents equilibrium in the goods market. It is derived from the Keynesian cross model and shows combinations of interest rates (r) and levels of income (Y) where planned spending equals output. The equation of the IS curve can be expressed as:
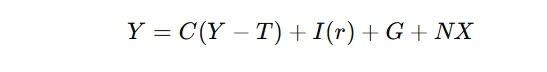
Where:
- Y: National income
- C(Y−T): Consumption, dependent on disposable income(Y−T)
- I(r): Investment, negatively related to the interest rate (r)
- G: Government spending
- NX: Net exports
The IS curve slopes downward because a lower interest rate stimulates investment, increasing aggregate demand and income.
What is the LM Curve?
The LM curve represents equilibrium in the money market, where money demand equals money supply. The equation for the LM curve is:
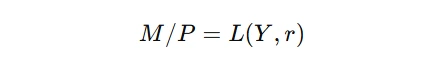
Where:
- M/P: Real money supply (nominal money supply divided by the price level)
- L(Y,r): Money demand, dependent on income (Y) and interest rates (r)
The LM curve slopes upward because higher income levels increase money demand, which raises interest rates for a fixed money supply.
The Interaction of IS and LM Curves
The intersection of the IS and LM curves determines the equilibrium level of income (Y) and the interest rate (r) in an economy. This equilibrium is crucial for understanding macroeconomic conditions and policy impacts.
When solving IS-LM problems in your exams, you must analyze how changes in fiscal policy (affecting the IS curve) or monetary policy (affecting the LM curve) shift these curves and influence equilibrium. Let’s explore common scenarios in IS-LM curve questions and the steps to approach them systematically.
Common Types of IS-LM Curve Problems
IS-LM problems in economics exams often test your ability to analyze shifts in curves, solve equations, and interpret macroeconomic outcomes. Here are the most common types of problems:
- Deriving the IS and LM Equations
- Policy Analysis
- How does an increase in government spending affect the IS curve?
- What happens to the LM curve if the central bank increases the money supply?
- Graphical Analysis
- Draw the IS-LM diagram
- Show shifts in curves due to specific policy changes or external shocks
- Indicate the new equilibrium points
- Comparative Statics
In some questions, you will be asked to derive the IS and LM equations from given functions, such as consumption, investment, and money demand. This requires a solid understanding of how the equations for the goods market and money market interact.
These questions typically involve fiscal or monetary policy changes and their impact on equilibrium income and interest rates. For example:
Graphical representation is a critical part of IS-LM problems. You might be asked to:
These problems require you to compare equilibrium before and after a policy intervention. This analysis helps demonstrate how fiscal or monetary policies influence macroeconomic variables like income and interest rates.
If you find these types of questions overwhelming, consider seeking online exam help to clarify your doubts and build confidence.
Step-by-Step Guide to Solving IS-LM Curve Problems
To approach IS-LM curve problems with confidence, follow this structured method:
Step 1: Read the Question Carefully
The first step in any exam problem is to thoroughly understand the question. Identify whether the problem focuses on:
- Shifts in the IS or LM curve
- Policy impacts
- Solving equations
Highlight key terms and data points given in the problem. A clear understanding of what’s being asked will guide your solution.
Step 2: Understand the Underlying Economic Scenario
Before jumping into calculations or graphs, interpret the economic scenario. Ask yourself:
- Is the problem dealing with fiscal or monetary policy?
- Are we analyzing an external shock (e.g., changes in consumer confidence or inflation)?
- What is the expected direction of shifts in the IS or LM curve?
Having a clear picture of the scenario will help you determine the correct approach.
Step 3: Set Up the Equations
Write down the relevant equations for the IS and LM curves based on the given data. For example:
IS Curve
- If the consumption function is and the investment function is , substitute these into the IS equation.
LM Curve
- Use the money demand equation to set up the LM curve.
Step 4: Solve for Equilibrium
Equilibrium occurs where the IS and LM curves intersect. To find the equilibrium values of income (Y) and interest rate (r):
- Equate the IS and LM equations.
- Solve the resulting system of equations simultaneously.
For instance, if the IS curve is and the LM curve is , solve for and :
Step 5: Draw the Diagram
Accurate and neat diagrams are essential for IS-LM problems. Follow these steps:
- Label the axes: Interest rate (r) on the vertical axis and income (Y) on the horizontal axis.
- Plot the IS curve as a downward-sloping line.
- Plot the LM curve as an upward-sloping line.
- Mark the equilibrium point and label it clearly.
If there are shifts, use arrows to indicate the direction of the movement. Ensure that your diagram matches the theoretical expectations discussed in class or your textbooks.
Step 6: Analyze the Results
Interpret your solution in the context of the question. For example:
- If fiscal policy increases government spending, explain how it shifts the IS curve to the right and raises equilibrium income and interest rates.
- If monetary policy increases the money supply, explain how it shifts the LM curve to the right, lowering interest rates and raising income.
Step 7: Check Your Work
Finally, verify your calculations and ensure your diagrams match the theoretical expectations. Double-check for any missing steps or errors. A final review can save you from costly mistakes in your exam.
Tips to Excel in IS-LM Problems
Here are some practical tips to approach IS-LM curve problems effectively:
- Master the Basics Ensure you have a strong grasp of macroeconomic fundamentals, including the Keynesian cross, money demand, and the role of fiscal and monetary policies. A clear understanding of these concepts will make IS-LM problems much easier to tackle.
- Practice Regularly Solving a variety of IS-LM problems will improve your problem-solving speed and accuracy. If you’re struggling with practice questions, consider using online exam help to work through challenging examples.
- Memorize Key Relationships Remember how changes in policies or external shocks affect the IS and LM curves:
- Expansionary fiscal policy shifts the IS curve to the right.
- Contractionary monetary policy shifts the LM curve to the left.
- Stay Calm Under Pressure If you’re overwhelmed during the exam, break the problem into smaller steps and tackle them one at a time. Focusing on one part at a time can help you stay composed and solve the problem systematically.
- Seek Help When Needed If you’re wondering, “Can someone take my economics exam?” or if you’re stuck on a specific topic, professional tutors can provide personalized guidance. Online platforms offer valuable resources to help you succeed in your exams.
Why Seek Online Exam Help for IS-LM Curve Problems?
IS-LM curve problems can be intricate and demand a deep understanding of both theoretical and practical aspects of macroeconomics. Sometimes, despite your best efforts, you may find yourself struggling with complex equations or diagram interpretations. Here are a few reasons why seeking online exam help can be beneficial:
- Expert Guidance: Professionals offering online exam help are well-versed in macroeconomic theories and can break down even the most challenging IS-LM problems into simpler steps.
- Time Management: If you are running out of time to prepare for your exams, seeking help ensures that you get personalized assistance tailored to your exam needs.
- Improved Accuracy: Economics exams require precise answers and well-drawn diagrams. An expert can help you refine your problem-solving techniques to achieve better accuracy and presentation.
- Stress Relief: Preparing for exams can be stressful, especially when dealing with topics like IS-LM curves. Expert guidance can help you stay calm and focused on achieving your desired grades.
- Customized Learning: Online platforms can cater to your unique learning needs by offering targeted solutions to your specific queries. If you’ve ever wondered, “Can someone take my economics exam?” professional assistance ensures that you’re in safe hands.
Conclusion
Mastering IS-LM curve problems in economics exams requires a thorough understanding of the theoretical foundations, careful analysis of problem scenarios, and consistent practice. By following the step-by-step guide provided in this blog, you can tackle these problems with confidence and precision. Additionally, tips like mastering the basics, practicing regularly, and seeking online exam help when necessary can significantly improve your performance.
If you’re still feeling overwhelmed or need personalized guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out for expert assistance. Whether it’s understanding complex shifts in the IS and LM curves or solving equilibrium equations, there’s always help available to ensure you achieve success in your economics exams.
So, the next time you face IS-LM curve problems, approach them systematically, stay calm under pressure, and remember that professional guidance is just a click away. With the right strategies and resources, you’ll be well on your way to acing your exams!